Module structure
This section will show:
Overview of modules
Conventions: dimension of nodes, objects and vectors
Coordinates: reference coordinates and displacements
Nodes, Objects, Markers and Loads
For an introduction to the solvers, see Section Solvers.
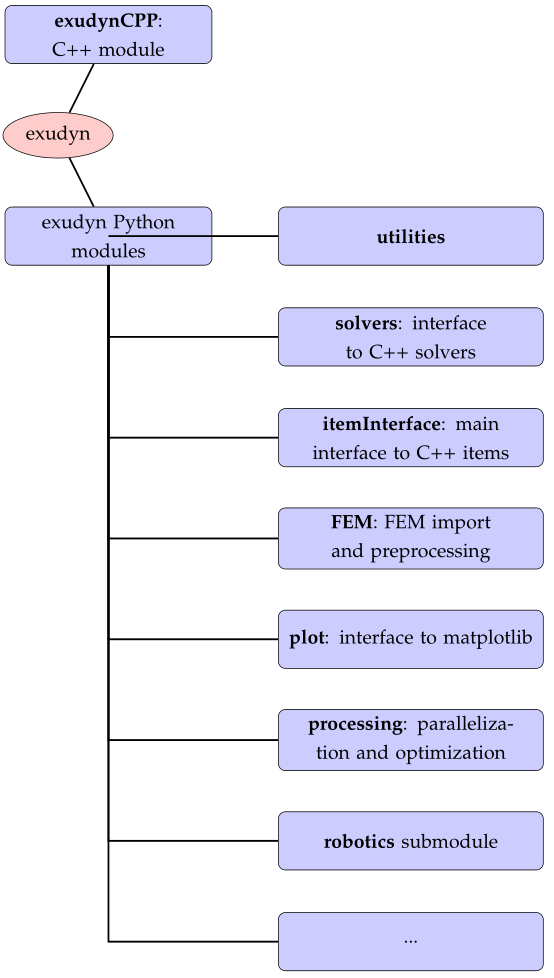
Fig. 1 Overview on Exudyn C++ and Python modules
Overview of modules
Currently, the Exudyn module structure is split into a C++ core part and a set of Python parts, see Fig. 1.
exudyn: on this level, there are just very few functions:SystemContainer(),SC.renderer.Start(),SC.renderer.Stop(),SolveStatic(...),SolveDynamic(...), … as well as system and user variable dictionariesexudyn.variablesandexudyn.sys
config,special: substructures for configuration (global settings) and special settings; use e.g.exudyn.config.outputPrecision=4
symbolic: tools for symbolic computation in user functions (speedup!)
SystemContainer: contains the systems (most important), solvers (static, dynamics, …), visualization settings
MainSystemmbs: mbs created withmbs = SC.AddSystem(), this structure contains everything that defines a solvable multibody system; a large set of nodes, objects, markers, loads can added to the system, see Section Items reference manual;
mbs.systemData: contains the initial, current, visualization, … states of the system and holds the items, see Fig. 3
SimulationSettings: contains the systems (most important), solvers (static, dynamics, …), visualization settings
Python parts (this list is continuously extended, see Section Python Utility Functions):
exudyn.artificialIntelligence: interface to stablebaselines, interface to pytorch training (coming soon)
exudyn.basicUtilities: contains basic helper classes, without importing numpy
exudyn.beams: helper functions for creation of beams along straight lines and curves, sliding joints, etc.
exudyn.graphics: provides some basic drawing utilities, definition of colors and basic drawing objects (including STL import); rotation/translation of graphicsData objects
exudyn.interactive: helper classes to create interactive models (e.g. for teaching or demos)
exudyn.itemInterface: contains the interface, which transfers Python classes (e.g., of a NodePoint) to dictionaries that can be understood by the C++ module
exudyn.FEM: everything related to finite element import and creation of model order reduction flexible bodies
exudyn.lieGroupBasics: a collection of Python functions for Lie group methods (SO3, SE3, log, exp, Texp, …)
exudyn.mainSystemExtensions: mapping of some functions to MainSystem (mbs)
exudyn.physics: containing helper functions, which are physics related such as friction
exudyn.plot: contains PlotSensor(…), a very versatile interface to matplotlib and other valuable helper functions
exudyn.processing: methods for optimization, parameter variation, sensitivity analysis, etc.
exudyn.rigidBodyUtilities: contains important helper classes for creation of rigid body inertia, rigid bodies, and rigid body joints; includes helper functions for rotation parameterization, rotation matrices, homogeneous transformations, etc.
exudyn.robotics: submodule containing several helper modules related to manipulators (robotics,robotics.models), mobile robots (robotics.mobile), trajectory generation (robotics.motion), etc.
exudyn.signalProcessing: filters, FFT, etc.; interfaces to scipy and numpy methods
exudyn.solver: functions imported when loadingexudyn, containing main solvers
exudyn.utilities: constains helper classes in Python and includes Exudyn main modulesbasicUtilities,rigidBodyUtilities,graphics, anditemInterface, which is recommended to be loaded at beginning of your model file in order to have most necessary functionality at hand
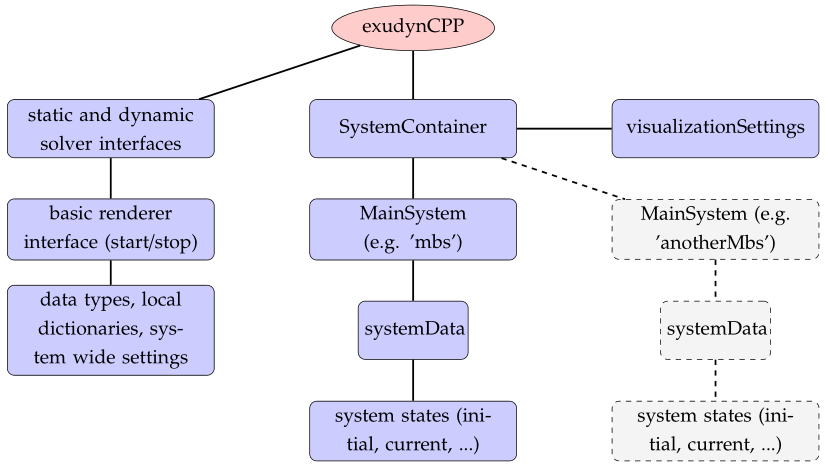
Fig. 2 Overview on Exudyn C++ module
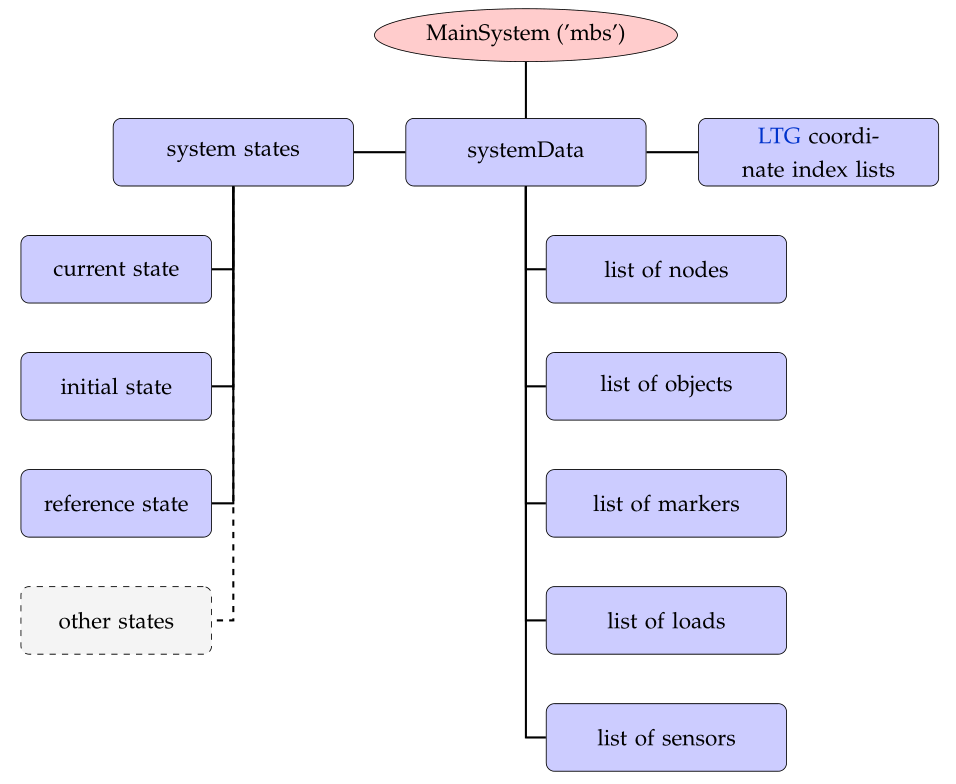
Fig. 3 Overview of systemData
SystemData connects items, states and stores the LTG. Note that access to items is provided via functions in MainSystem.
Conventions: items, indexes, coordinates
In this documentation, we will use the term item to identify nodes, objects, markers, loads and sensors:
item \(\in\) {node, object, marker, load, sensor}
Indexes: arrays and vectors starting with 0:
As known from Python, all indexes of arrays, vectors, matrices, … are starting with 0. This means that the first component of the vector v=[1,2,3] is accessed with v[0] in Python (and also in the C++ part of Exudyn ). The range is usually defined as range(0,3), in which ‘3’ marks the index after the last valid component of an array or vector.
Dimensionality of objects and vectors: 2D vs. 3D
As a convention, quantities in Exudyn are 3D, such as nodes, objects, markers, loads, measured quantities, etc. For that reason, we denote planar nodes, objects, etc. with the suffix 2D, but 3D objects do not get this suffix(There are some rare exceptions, such as Beam3D as the pure beam may easily lead to name space conflicts in Python).
Output and input to objects, markers, loads, etc. is usually given by 3D vectors (or matrices), such as (local) position, force, torque, rotation, etc. However, initial and reference values for nodes depend on their dimensionality.
As an example, consider a NodePoint2D:
referenceCoordinatesis a 2D vector (but could be any dimension in general nodes)measuring the current position of
NodePoint2Dgives a 3D vectorwhen attaching a
MarkerNodePositionand aLoadForceVector, the force will be still a 3D vector
Furthermore, the local position in 2D objects is provided by a 3D vector. Usually, the dimensionality is given in the reference manual. User errors in the dimensionality will be usually detected either by the Python interface (i.e., at the time the item is created) or by the system-preprocessor